In the early days of SEO, the game was simple.
Find a keyword with high volume, stuff it into your H1 tag five times, and wait for the traffic. It was a game of “matching strings.”
In 2026, Google’s AI (Gemini and MUM) doesn’t just match strings; it matches goals. If you search for “Apple,” Google knows whether you want the fruit, the tech giant, or the 1960s record label based on context.
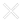
For an SEO company, this shifts the battlefield entirely. We are no longer fighting for “Keywords”; we are fighting for “Intent.”
If your agency is still selling you a list of 50 high-volume keywords without mapping the user journey, they are selling you the old-school metrics. Traffic without intent is just noise. It costs money to host, but it generates zero revenue.
Here is why mastering search intent SEO is a vital part of an SEO strategy in 2026
Table of Contents
- Why Relying on Only Keywords Does Not Work
- What Are the 4 Pillars of Search Intent?
- How Does Google Actually Read Minds in 2026?
- How Can You Identify Intent Before You Write?
- How Do You Map Intent to the Sales Funnel?
- Why Does Intent Matter for an SEO Company in India?
- How Do We Measure Success Beyond Rankings?
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Why Relying on Only Keywords Does Not Work
Relying solely on keywords fails because modern technology has shifted from simple text matching to intent satisfaction
1. Search Engines Now Focus on Intent, Not Just Words
Source: Clearscope
Search engines like Google now use semantic search to understand the meaning and context behind a query.
Ambiguity:
A keyword like “Apple” could mean the fruit or the technology company. Without context, a keyword-only system cannot tell the difference.
User Goals:
Someone searching for “best cameras” usually wants product comparisons. Someone searching for “how to clean a lens” needs a step-by-step guide. If a page is stuffed with keywords but does not match the user’s intent, it will rank lower.
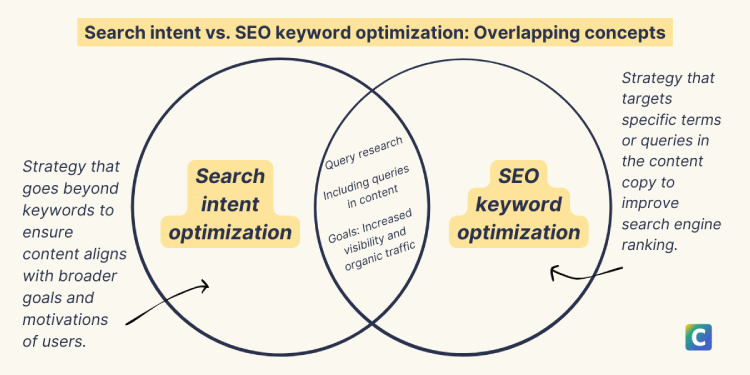
2. The Keyword Research Trap
Focusing only on high-volume keywords can bring traffic that does not convert into customers.
Irrelevant Traffic:
You may rank for a popular term, but if the visitor’s goal does not match your offer, they will quickly leave the page.
Inaccurate Data:
Broad match settings in tools like Google Keyword Planner can inflate search volumes. This can lead to wrong strategic decisions.
3. Limitations of Traditional Keyword Search
Keyword-based systems are rigid and often miss relevant information that uses different wording.
Synonyms and Variations:
A search for “vacation” may miss content that uses the word “holiday” unless both are specifically targeted.
Zero Result Searches:
Users who do not know the exact technical terms often fail to find what they need in keyword-only systems.
4. Modern Search Is Conversational
With AI overviews and voice assistants, search queries are becoming longer and more detailed.
Multi-step Queries:
Users now ask complex questions such as, “What is the best laptop for a student under $1000 that can also handle video editing?” Keywords alone cannot properly understand multiple conditions in one query.
Semantic Understanding:
Modern systems convert queries into numerical representations of meaning. This allows them to find conceptually relevant content, even if the exact keywords are not present.
This “Pogo-sticking” (bouncing back to the search results) sends a signal to Google: “This website is irrelevant.” Google then downgrades your rankings, not just for that keyword, but often for your domain authority as a whole.
An experienced SEO company that focuses on intent ensures that when a user lands, they stay. We don’t want all the traffic; we want the right traffic.
What Are the 4 Pillars of Search Intent?
To optimise for intent, you must understand the four distinct “modes” a user’s brain is in when they type a query.
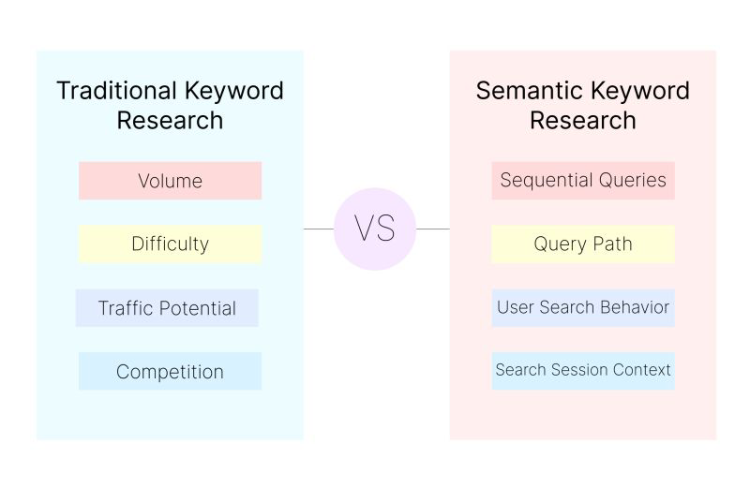
1. Informational Intent (The Learner)
- The Query: “How to tie a tie” or “What is SEO?”
- The Goal: To learn. They are not ready to buy.
- The Content: Comprehensive guides, “How-To” videos, and definitions.
2. Navigational Intent (The Navigator)
- The Query: “Facebook login” or “Flora Fountain blog on top SEO Strategies.”
- The Goal: To get to a specific place.
- The Content: Clear, fast-loading login pages or homepages. You generally cannot “rank” for these unless you are the brand.
3. Commercial Investigation (The Comparator)
- The Query: “Best CRM for small business 2026” or “iPhone 16 vs Samsung S25.”
- The Goal: They are ready to buy but need help choosing.
- The Content: Comparison tables, “Best of” lists, and detailed reviews.
4. Transactional Intent (The Buyer)
- The Query: “Buy Nike Air Max online” or “SEO agency pricing.”
- The Goal: To complete a purchase now.
- The Content: Product pages with “Add to Cart” buttons or “Book a Call” forms.
How Does Google Actually Read Minds in 2026?
Google’s algorithm has evolved from a filing cabinet to a detective. Updates like BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) and MUM (Multitask Unified Model) allow Google to understand nuance.
1. Intent Extraction Through Query Fan-Out
Instead of processing just one keyword, Google’s AI now expands your query using a method called query fan-out.
Sub-Search Generation:
For every search, the system creates 5 to 10 related sub-searches to understand the full context. For example, if you search for “scaling revenue operations,” it may also explore topics like headcount, technology stack, and fractional leadership.
Goal-Focused Results:
The system tries to understand why you are searching, not just what you typed. Results are shaped around your overall goal.
2. Behavioural and Interaction Signals
Google now understands intent by studying how you interact with your device.
Contextual Patterns:
It looks at how you scroll, tap, click, and even how long you pause on certain content.
On-Device Processing:
Much of this analysis happens directly on your device instead of the cloud. This improves both speed and privacy.
Pre-Search Behaviour:
Your activity before typing a query can help predict what you are likely to search next.
3. Hyper-Personalisation as the New Standard
Search results are becoming personalised rather than generic. Two people asking the same question may see very different results.
Layered Learning:
Short-term signals, such as current session behaviour, work together with long-term models of how you make decisions.
User Preferences:
AI considers your past behaviour, budget, location, and preferences, such as sustainability. It then adjusts the results page accordingly.
4. Predictive and Agent-Based Search
Search is moving from reactive to proactive.
Predictive Suggestions:
By analysing your calendar and emails, AI assistants may suggest solutions before you even search. For example, it may recommend flight options for a meeting already on your schedule.
Agent-Based Search:
AI systems can now manage the full customer journey. This includes discovery, comparison, and even checkout within one conversation.
5. Trust and Inference Confidence
As AI-generated content increases, trust becomes more important.
Brand Authority Over Keywords:
It matters more for a brand to be recognised as a trusted entity than to simply rank for specific keywords.
Verification Signals:
Google uses advanced reasoning systems to evaluate the credibility of landing pages. Verified sources are more likely to appear in high-trust AI-driven search experiences.
This means your content cannot just contain the keywords; it must solve the problem.
How Can You Identify Intent Before You Write?
You don’t need a crystal ball or a tarot card reader; you just need to look at the SERP (Search Engine Results Page). Google has already done the heavy lifting. Before writing a single word, a smart search intent optimization agency performs “SERP Forensics.”
- Scenario A: You search for a keyword and see a Video Carousel at the top.
- Insight: Google knows users want to watch the answer, not read it. Writing a 2,000-word blog here is a waste of time. Make a video.
- Scenario B: You search and see a “People Also Ask” box with definition questions.
- Insight: The intent is Informational. Don’t try to sell your product in the first paragraph.
- Scenario C: You search and see Google Shopping Ads.
- Insight: The intent is Transactional. Optimize your product schema, not your blog.
How Do You Map Intent to the Sales Funnel?
A mature SEO strategy does not just “get traffic.” It moves users from “Curious” to “Customer.” To do this, you must map specific search intents to the three stages of your marketing funnel. We call this User Journey Mapping.
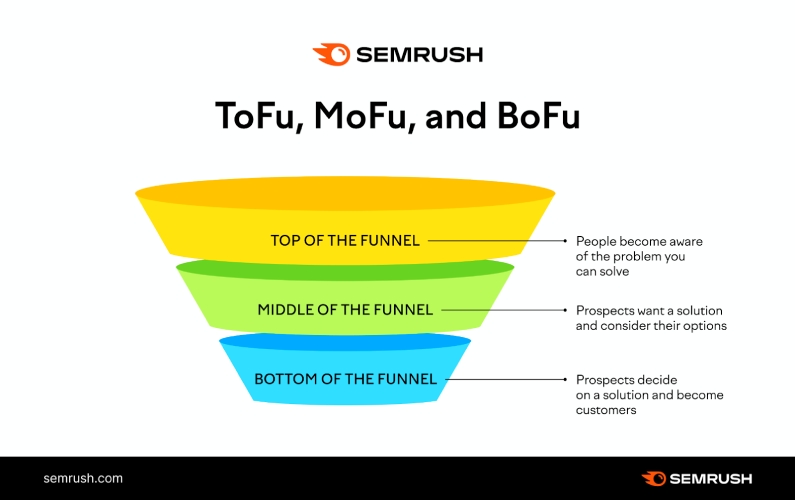
1. Top of Funnel (ToF): The Awareness Stage
- The User Mindset: “I have a problem, but I don’t know the solution yet.” They are looking for education, not a sales pitch.
- The Intent: Informational (“Know” moments).
- Keyword Signals: What is, How to, Why, Guide, Tips, Examples.
- The Content Asset:
- “Ultimate Guides”: Comprehensive, long-form blogs (2,000+ words) that cover a topic exhaustively.
- “Definition” Pages: Short, snippet-optimised glossary terms.
- Checklists & Templates: Downloadable assets that solve a quick pain point.
- The Goal: Capture traffic, build authority, and “pixel” the visitor for future retargeting ads.
2. Middle of Funnel (MoF): The Consideration Stage
- The User Mindset: “I know the solution (e.g., ‘I need SEO’), but who is the best provider?” They are evaluating options and comparing you against competitors.
- The Intent: Commercial Investigation (“Compare” moments).
- Keyword Signals: Best, Top 10, Vs, Reviews, Alternatives, Case Study.
- The Content Asset:
- Comparison Pages: Honest “Us vs. Them” tables (e.g., “Flora Fountain vs. Freelancers”).
- “Best Of” Listicles: Curated lists where you feature your product alongside others (yes, even competitors) to build trust.
- Case Studies: Detailed “Before & After” stories that prove your expertise with data.
- The Goal: Differentiate your brand and capture email leads (e.g., “Download our Case Study”).
3. Bottom of Funnel (BoF): The Decision Stage
- The User Mindset: “I am ready to buy. Give me the offer.” They want to minimise risk and complete the transaction.
- The Intent: Transactional (“Do” moments).
- Keyword Signals: Buy, Price, Cost, Quote, Agency near me, Consultation, Discount.
- The Content Asset:
- Service/Product Pages: High-conversion landing pages with clear value propositions and trust badges.
- Pricing Pages: Transparent breakdown of costs (or a “Get a Quote” calculator).
- “Book a Demo” Pages: Frictionless forms designed for speed.
- The Goal: Revenue. These pages should have zero distractions—just a clear path to the checkout or calendar.
Why Does Intent Matter for an SEO Company in India?
In a market like India, why do SEO companies focus on search intent over keywords? It is a critical question. The Indian user is unique.
- The “Hinglish” Factor: Users often type “Best shoes under 2000 mein.” An intent-focused agency optimises for this natural language, not just the English dictionary version.
- Hyper-Specific Voice Search: Indian users are heavy users of Voice Search (“Okay Google, mere paas best pizza kaunsa hai?”). These queries are long-tail and highly transactional. Keywords fail here; intent wins.
- The “Trust” Hurdle: Indian users are sceptical. Intent-based content that educates before it sells builds the trust required to close a deal in this market.
How Do We Measure Success Beyond Rankings?
If we stop obsessing over keywords, what do we measure?
We track Engagement Metrics that prove we satisfied the intent.
- Dwell Time: Are they spending 3+ minutes reading the guide? (Success).
- Scroll Depth: Did they read 75% of the page? (Success).
- Conversion Rate: Did the “Commercial” intent traffic actually fill out the form? (Success).
- Bounce Rate (Contextual): A high bounce rate on a “Contact Us” page is fine (they got the number and left). A high bounce rate on a “Guide” is bad.
Conclusion
Keywords are the map; Intent is the destination. You can have the best map in the world, but if it leads the user to a destination they didn’t want to visit, they will leave.
In 2026, the best SEO company is the one that acts as a tour guide, leading the user to exactly what they are looking for, at the exact moment they need it. Stop optimising for robots. Start optimising for humans.